

Special centers in the brain stem also help control breathing and the beating of the heart. It contains bundles of very long nerve fibers that carry signals controlling muscles and sensation or feeling between the cerebrum and the rest the body. The brain stem is the lower part of the brain that connects to the spinal cord. Tumors of the cerebellum can cause problems with coordination in walking, trouble with precise movements of hands, arms, feet, and legs, problems swallowing or synchronizing eye movements, and changes in speech rhythm. The cerebellum lies under the cerebrum at the back part of the brain. The cerebellum is the second-largest region of the brain, constituting about 10% of its volume but containing over 50% of its neurons. It is also marked by fissures, sulci, and gyri (called folia in the cerebellum). The cerebellum occupies the posterior cranial fossa inferior to the cerebrum, separated from it by the transverse cerebral fissure. It is also responsible for planned (voluntary) muscle movements (throwing a ball, walking, chewing, etc.) and for taking in and interpreting sensory information such as vision, hearing, smell, touch, and pain. The cerebral hemispheres control reasoning, thought, emotion, and language. At the bottom of this fissure, the hemispheres are connected by a thick bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum-a prominent landmark for anatomical description with a distinctive C shape in sagittal section. A very deep median groove, the longitudinal fissure, separates the right and left hemispheres from each other. Each hemisphere is marked by thick folds called gyri (singular, gyrus) separated by shallow grooves called sulci (singular, sulcus). The cerebrum is about 83% of the brain’s volume and consists of a pair of half globes called the cerebral hemispheres. The cerebrum is the large, outer part of the brain.
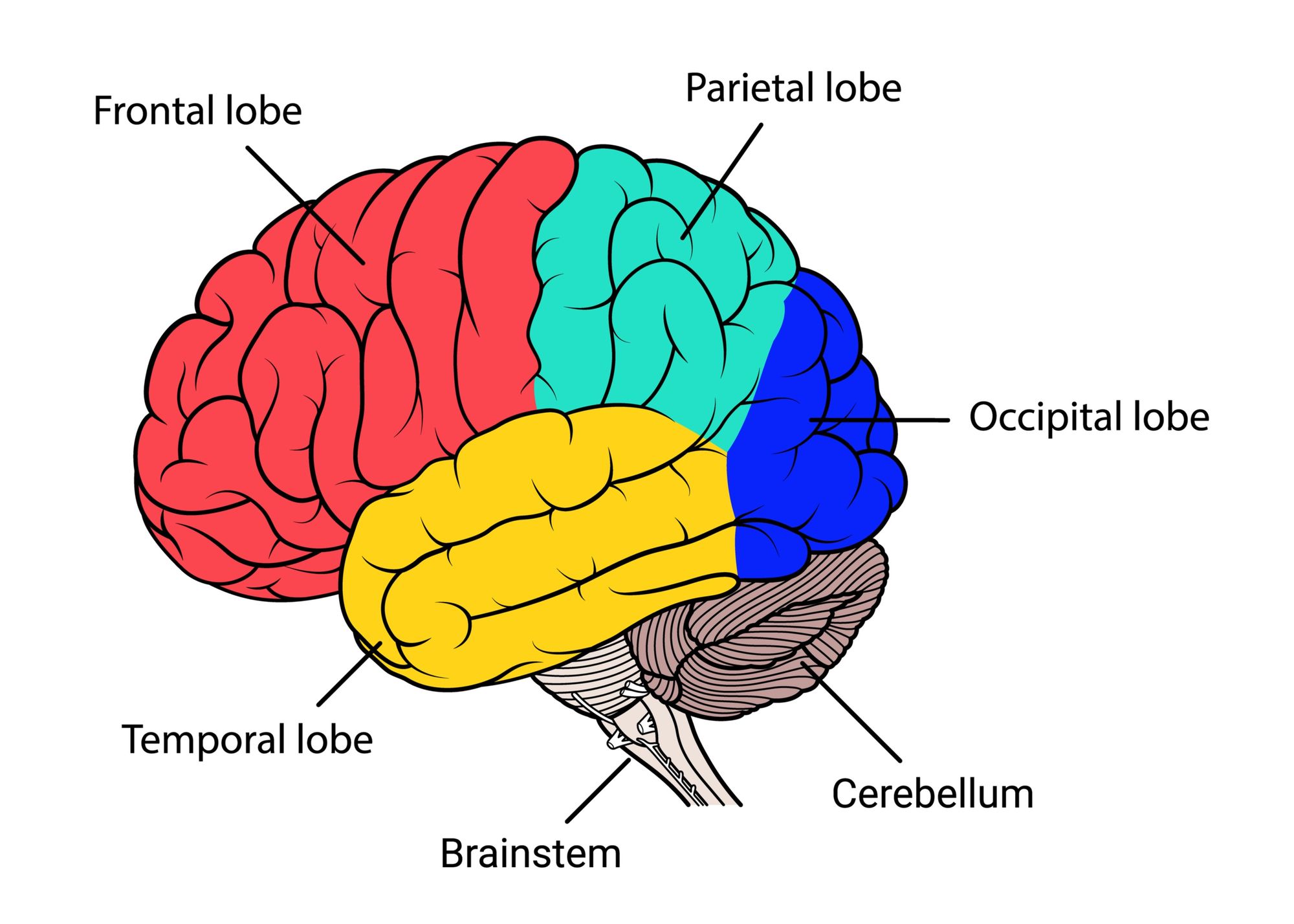

As in the spinal cord, white matter is composed of tracts, or bundles of axons, which here connect one part of the brain to another and to the spinal cord.įigure 3. White matter lies deep to the cortical gray matter in most of the brain, opposite from the relationship of gray and white matter in the spinal cord. Gray matter-the seat of the neurosomas, dendrites, and synapses-forms a surface layer called the cortex over the cerebrum and cerebellum, and deeper masses called nuclei surrounded by white matter. The brain, like the spinal cord, is composed of gray and white matter. Together, the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system ) control the physiological and psychological functions of your body. The brain stem connects the brain to the spinal cord, and controls breathing, heart rate, and the nerves and muscles that we use to see, hear, walk, talk, and eat. The cerebellum controls movement, balance, and posture. The Diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus).The cerebrum controls thinking, learning, problem solving, emotions, speech, reading, writing, and voluntary movement. The organs of the central nervous system (CNS) can be divided into two groups, the brain and the spinal cord.Īnatomists conceptually divide the brain into four major parts: The difference between the sexes is proportional to body size, not intelligence. The human brain is roughly the size of two clenched fists and weighs about 1.6 kg (3.5 lb) in men and 1.45 kg in women 1). The human brain is a component of the central nervous system. Blood Supply to the Brain and the Brain Barrier System.Cerebral Gray Matter (Functional Areas of the Cerebral Cortex).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
